
This article is inspired by the
Aurora's introduction of the LED's -
the LED technology,
the LED colour variation,
the features and benefits of the LEDs,
the history of the LEDs, and some of the most
common applications of the LED lamps. Since it is a technology in a continual development, this article is just a theoretical initial introduction - with the current
dimmable LEDs and
coloured RGB LED strips, etc - there will be more information posted soon.
- The LEDs are solid state semiconductor devices. The LED illumination is achieved when a semiconductor crystal is excited so that it directly produces visible light in a desired wavelength range (colour). LED's are small, typically 5mm.
- The light from an LED is practically a pure, single colour. A green LED produces green light only, a red LED only red light, and so on.
- It is the material of the LED chip that determines the colour. The LED's are driven by direct current, and the amount of current determines the brightness. See the Colour Changing RGB LED strip.
- The brightness of the LED is proportional to the current flowing through the LED, more current, more light. In order to create a full range of colours including white light, we need to use a selection of different coloured LED's that can be combined in various proportions to create a wide colour palette.
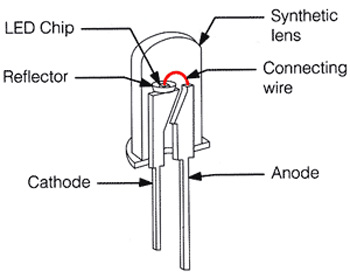 A schematic image of the LED
A schematic image of the LED
- The LED Chip;
- The LED Reflector;
- The LED Cathode;
- The LED Synthetic Lens;
- The LED Connecting Wire;
- The LED Anode.
- Energy Saving: The LEDs are extremely efficient low energy light sources;
- Light gains: In 2005 the white LEDs reached outputs of over 30 lumens / Watt and coloured versions 50 lumens / Watt. The light gains continue to grow - doubling about every two years;
- Long operational life: up to 50,000 hours;
- Compact light source: no other lamp possesses such small dimensions for a comparative light output;
- No radiation: the LEDs do not emit ultraviolet (UV) or infrared (IR) radiation. They do not radiate heat in the direction of the illuminated object - they can be used to illuminate materials that fade easily like food, works of art etc.
- Durable lamps: The LEDs are durable against impact and vibration;
- Dimmable LEDs: the LEDs can be dimmed;
- Coloured lamps: Coloured light can be produced effectively - over 16 million colours.
Due to the manufacturing process of LED’s they are graded into ‘
Bins’ of like colour temperature. Even within these ‘Bins’ it is impossible to guarantee the colour temperature of the light. This colour variation can be discernable to the human eye and this should be taken into account when designing lighting plans using LED technology.
- In 1907 - Henry Joseph Round discovered the physical effect of electro-luminescence;
- In 1962 - The first red luminescent diode appears on the market. The industrially produced LED is born;
- In the 1970's - the LEDs are available in further colours : Green, orange and yellow;
- In the 1980's - to early 1990's - high performance LED's (LED modules) in red, orange, yellow and green become available;
- In 1995 - the first LED producing white light by luminescence conversion is launched;
- In 1997 - the white LEDs become commercially available;
- LED lamps used in Display lighting - compact displays are possible with low operating temperatures(example: the Illuma Shaker Spotlights, LED track spots);
- LEDs used in display case, museum and shop lighting - for the illumination of sensitive objects at close range with ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) free light(example: the IllumaLED Shaker Track Spotlights);
- LED lamps used in underwater lighting - a low voltage supply for safety and low maintenance(example: Underwater LED lights, high IP rated LED lamps);
- LEDs used in outside lighting - the LEDs offer coloured effects to enhance outdoor spaces(example: the LED garden lights, walkover lights);
- LED lamps used in sign lighting - the strips of LEDs can be used for light signage in many different colours(example: the LED strips used for sign lighting outdoors);
- LEDs used in low level lighting - the LED luminaires are cool to touch and are therefore suitable for use in domestic situation where children may come in contact with them(example: the domestic non-threatening LED lamps);
- LED lamps used in architectural detail lighting - the LED's can be used in applications which traditionally used neon or cold cathode.
You can purchase many of
the LED lamps via -
LED Outdoor Lights,
LED Wall Lamps,
LED Table Lamps,
LED Strip Lights, etc. Browse through our website and see if the fitting you're looking for is in its LED lamp version.
 This article is inspired by the Aurora's introduction of the LED's - the LED technology, the LED colour variation, the features and benefits of the LEDs, the history of the LEDs, and some of the most common applications of the LED lamps. Since it is a technology in a continual development, this article is just a theoretical initial introduction - with the current dimmable LEDs and coloured RGB LED strips, etc - there will be more information posted soon.
This article is inspired by the Aurora's introduction of the LED's - the LED technology, the LED colour variation, the features and benefits of the LEDs, the history of the LEDs, and some of the most common applications of the LED lamps. Since it is a technology in a continual development, this article is just a theoretical initial introduction - with the current dimmable LEDs and coloured RGB LED strips, etc - there will be more information posted soon.
 A schematic image of the LED
A schematic image of the LED


